| Developers: | Kioxia Europe (ранее Toshiba Memory Europe, TME), Kioxia (formerly Toshiba Memory) |
| Date of the premiere of the system: | 2018/05/18 |
| Last Release Date: | 2021/06/22 |
| Technology: | SHD |
Content |
White Paper: Storage
2021: Version 3.18
On June 22, 2021, Kioxia Europe announced the release of version 3.18 of its platform for data centers KumoScale based on the NVMe-oF protocol (NVM Express over Fabrics). The KumoScale platform is designed for data center-wide deployment and provides an NVMe flash memory system (NVM Express) in the form of a disparate network service.
According to the company, ON KumoScale version 3.18 supports built-in integration with an updated version of OpenStack Infrastructure Wallaby Release.
KIOXIA is actively involved in the Development Community OpenStack (OpenStack Contributor Community) and has already managed to make a number of changes to this open-source infrastructure source code that are designed to ensure the integration of NVMe-oF storage resources. The contribution of KIOXIA involves two important tasks related to storages NVMe-oF in the environment: OpenStack
- in previous versions, the connector NVMe-oF within the framework of the infrastructure OpenStack created a resource-intensive connection for each of the volumes, even if they had a common goal, which is why deployments NVMe-oF imposed certain requirements on computing and network resources;
- in previous versions, os-brick OpenStack did not use md-raid client capabilities to write directly to replicated volumes in multiple vaults.
To provide built-in NVMe-oF support, KIOXIA has made the following changes to the OpenStack Infrastructure Wallaby Release code:
- rebuilt the software code of the connector OpenStack os-brick NVMe-oF (nvmeof.py) and added support for newer protocols NVMe-oF;
- Optimized OpenStack Infrastructure Wallaby Release header to support client-side volume replication via md-raid
- Optimized Cinder driver for KumoScale software that integrates KumoScale storage into OpenStack environments.
| The NVMe-oF protocol is increasingly used in modern network architectures of the data center, so we are pleased to introduce the release of KumoScale within the framework of the software stack. said Frederik Haak, Director of SSD Promotion at KIOXIA Europe |
| Developers and users Cinder are grateful to KIOXIA specialists for their technical contribution to the Cinder project, which made it possible to implement the OpenStack Block Storage service. These functions will open up to the community OpenStack the capabilities of the NVMe-oF protocol. told Brian Rosmaita, head of the development team OpenStack Cinder (PTL) and lead programmer Red Hat |
Among other things, version 3.18 includes a trial technical version of the built-in support for the border routing protocol (BGP), implemented through the integration of ON Free Range Routing (FRR) network routing. So it was possible to provide the first in the industry function of transmission data over multi-track TCP networks/for IP storage. NVMe-oF For packet transmission, such networks mainly use IP routing, and as of June 2021, one of the most popular routing protocols in such an environment is BGP. KumoScale supports BGP, so storage resources can act as a first-class object on the Clos network. This ensures proper connectivity between client-side senders and vaults. To connect to IP networks, the storage system uses Layer 2 technologies, such as a port channel. Instead, storage systems KumoScale operate at Layer 3 (that is, IP routing), so they can act as a built-in cloudy service in the data center network. As the protocol of routing KumoScale uses BGP, providing the routed mnogotraktovy network of the 3rd level between senders and KumoScale storages.
| As of June 2021, BGP is widely used in cloud data center environments, where a small team of specialists can support a large network due to ease of operation and connectivity. Due to the built-in support of BGP traffic for NVMe-oF, the storage receives support for the IP routing function. reported by Dinesh Dutt, author of the published book Cloud Native Data Center Networking |
Also ON KumoScale of version 3.18 includes a number of changes in processes of installation and updating, a complex security system and telemetry of the reporting. In addition, the sample software reporting panel KumoScale based on the Prometheus and Grafana telemetry platforms.
2020
Version 3.16
On November 25, 2020, the company KIOXIA Europe introduced the next version of its software storage KumoScale based on NVM Express over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) technology. Version 3.16 KumoScale provides support for PCIe 4.0 family components including servers NICs and SSDs (). SSD
Designed to double the performance of client, server, and storage systems, PCIe 4.0 provides new levels of performance for cloud and enterprise applications. KumoScale 3.16 takes advantage of the faster connections offered by PCIe 4.0, allowing cloud systems to serve more users per storage node and thus reduce operating costs.
Additional improvements included in version 3.16 include:
- A third-party application hosting platform that allows servers to KumoScale host storage services as a repository of files and objects so they can take advantage of KumoScale performance. In both environments, storage resources are KumoScale mapped to workloads as fast local NVMe volumes.
- Kubernetes CSI and OpenStack Cinder drivers that support basic storage features, snapshots, and thin provisioning.
- Dynamic Volume Migration: Runs on back-end servers while saving
data consistency and support dynamic workload migration.
- Multi-user virtual cluster support - Improves security by isolating client workloads.
| NVMe is becoming increasingly popular in server and storage systems. Starting with version 3.16, KumoScale offers PCIe 4.0 support and NVMe storage connectivity over a network with similar performance to a local storage device. Continuous improvements for integration into cloud orchestration platforms, such as Kubernetes and Open stack, are aimed at meeting the requirements for cloud applications, - says Frederik Haak, Senior Head of Solid-State Drive Marketing, KIOXIA Europe |
Version 3.14
On June 25, 2020, KIOXIA Europe announced the release of an updated version of the KumoScale storage management software, which is based on the NVM Express over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) protocol.
According to the company, the technology on which the work of KumoScale is based was first introduced in 2017. After a while she received certification of NVMe-oF of InterOperability Laboratory of the university of New Hampshire, engaged in tests and certification of technologies and the software of NVMe. KIOXIA (formerly Toshiba Memory Europe GmbH) brought the KumoScale to market in March 2018.
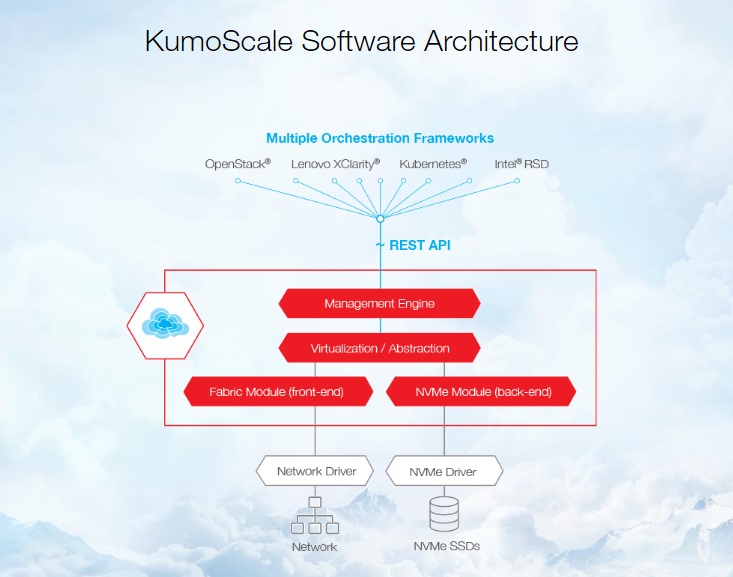
KumoScale software is a cloud-based solution that provides access to NVMe Flash blocks through an "intermediary" - virtual storage located between the customer and physical storage. The software is equipped with a central application programming interface (API) through which applications request the necessary resources. The program processes requests and dynamically allocates space, connecting only the required amount of flash memory for each task. The KumoScale software is based on the NVMe-oF standard, which provides performance comparable to when NVMe SSDs are locally connected. Also, it is an over Fabrics solution that supports clean deployment, virtualization, and the use of Kubernetes on various servers common in the industry as of June 2020 .
Features of version 3.14:
- Thin Provisioning. This technology allows you to allocate enough storage resources among servers. Unlike the traditional method, when the client receives the entire volume of empty blocks at once, KumoScale offers economical distribution, allocating additional data blocks if necessary. The use of Thin Provisioning technology allows you to reduce the amount of unused memory and increase the utilization of storage, which under the traditional approach can often be no more than 10% (in the traditional method, large capacities are allocated to individual servers, but remain unused (data on them are not written)).
- Self-healing. The volume recovery mechanism automatically detects and eliminates data inconsistencies that may result from replication failures, such as reconnecting to a target, incomplete deletion of replicas, and so on. This process does not require system administrator monitoring and intervention.
- Network fault tolerance. End-to-end multipath routing for TCP/IP network protocols provides complete network fault tolerance. KumoScale clients use Linux Link Aggregation Communications Protocol (LACP) and improved connection management to ensure consistent packet delivery across all available network paths. The KumoScale targets use port binding to increase availability and also maximize the overall capacity of the storage node.
- Automatic deployment of the storage node. PXE (Preboot eXecution Environment) support allows automatic network installation in environments. Data Center The ability to PXE-download eliminates the need for a bootable device, it is operating system not necessary and - ISOfile on a DVD or USB a device.
- Native NVMe snapshots. Native NVMe snapshots for deployments via Kubernetes CSI API and directly via REST API or CLI.
- Support for enterprise-class CM6 devices. Full support for the entire line of KIOXIA CM6 SSDs, which work in PCIe 4.0 (1 × 4, 2 × 2) and NVMe 1.4 modes, and provide consistent and arbitrary transfer rates up to 6.9 GB/s with a speed level of up to 1.4 million IOPS. Devices are optimal for use in areas such as databases, data analytics and artificial intelligence.
| By making NVMe a standard SSD protocol, you can use it more actively to deploy storage. Unbundling is important for an efficient storage infrastructure. KumoScale integrates into today's cloud and edge infrastructures. |
2018: Software Launch
On May 18, 2018, Toshiba Memory Europe (TME) announced the start of deliveries of KumoScale software designed for shared fast storage based on NVMe-oF technology (NVM Express over Fabrics). According to the developer, with KumoScale software, it becomes possible to use NVMe-oF technology to provide access to flash storage over the data center network by simply and flexibly abstracting physical disks to form a block storage pool while maintaining high performance of directly connected SSD disks with the NVMe interface.
| "Cloud-based, direct-attached SSD storage solutions are cost-effective and easy to deploy. The fixed nature of direct-attached storage can limit the flexibility afforded by the use of containers and their management infrastructure. The KumoScale software allows cloud data centers to scale and independently organize server and flash storage. This helps you adapt to unexpected and peak workloads, enabling your data centers to leverage new revenue opportunities with the flexibility and performance they need. " |
The technology that underpins KumoScale has been certified as software for storage systems that meet the NVMe-oF specification. The software KumoScale manages all the functionality of the system, allowing you to create networked storage nodes with immediate mass deployment, which increases the efficiency of using productive NVMe SSD drives by separating them. In addition, KumoScale paves the way for more efficient use of computing nodes through dynamic orchestration and provides high-performance storage for such a container management infrastructure as Kubernetes, also allowing the ability to adapt to in-house resource provision systems, TME noted.
| "In many cloud infrastructures, limitations in processing power and storage impede storage performance and scalability. The software KumoScale improves investment efficiency and operational flexibility. Cloud-based systems that work with real-time data analysis, financial applications, and NoSQL databases can leverage the capabilities of a split NVMe-oF structure to address these constraints while taking full advantage of an orchestrated container environment. " |