The main articles are:
2075: Forecast for 3rd largest GDP in the world at $51.5 trillion
2025: GDP decline by 0.3% in Q1 due to record volume of imports in anticipation of tariffs in foreign trade
US GDP decreased by 0.3% in the first quarter of 2025. This is the first decline from 1q22, when US GDP decreased by 1% q/q SA. The main reason for the decline is the record increase in imports on record.
It's all about the growth of imports with a negative contribution of 5.03 pp, it was worse only once - in 3q20 with a negative contribution of 7.46 pp.
Household consumption slowed to 1.21 pp in 1Q25 vs on average 2.1 pp per quarter in 2024, 1.59 pp in 2011-2019, 1.78 pp in 2017-2019 and 1.71 pp in 2022-2024.
The main reason for the slowdown in consumer demand is a sharp decrease in the growth rate of retail sales to 0.11 percentage points of a positive contribution with a medium-term rate of 0.8 percentage points in 2017-2019, while demand for services added 1.1 percentage points with a rate of 0.98 percentage points.
Gross private domestic investment increased sharply, providing a positive contribution of 3.6 pp vs + 0.31 pp in 2024, an average of 0.87 pp in 2011-2019, 0.65 pp in 2017-2019 and 0.22 pp in 2022-2024.
Such a sharp increase in investment is due to the growth of reserves, which provided 2.25 pp of a positive contribution to US GDP, while in 2024 business reduced reserves at a rate of 0.13 pp of a contribution to GDP.
At the same time, investments in fixed assets remained at a high level - 1.34 percentage points of a positive contribution vs + 0.44 percentage points in 2024.
State consumption and state investments made a negative contribution of 0.25 percentage points to the change in US GDP of 1qu25 vs + 0.55 percentage points in 2024.
The negative participation of the state in economic dynamics is associated with a reduction in defense spending and investment by 0.33 pp in 1Q25 vs + 0.26 pp in 2024 and + 0.11 pp in 2022-2024.
Thus, consumer demand is weakening, government consumption and investment are predominantly declining or at zero without defense spending, investment is growing through inventory changes, and net exports are the worst ever.
The US economy under Trump has sharply increased imports and is working in stock.
In fact, it is not the first time that GDP has declined, but usually everything ends within one quarter, for example, in 1q22 (-1%), 1q14 (-1.4%) and 1q11 (-0.9%), but this was always followed by growth.
2024
GDP growth by 2.3% at the end of the year. 68% is household consumption
The U.S. economy ended 2024 with 2.3% GDP growth thanks to consumers.
Trade in goods accounted for 18.4% of US GDP
In 2024, trade in goods as a share of GDP in China was recorded at 32.9%. For comparison, the United States has this figure of approximately 18.4%, and the European Union - 28%. This is stated in the Econovis review, published at the end of February 2025. Read more here.
Research and development, as well as the creation of IT form 5.1% of GDP
In the United States, the share of the research and IT segment in GDP is consistently growing. Research and development, as well as the creation of IT form 5.1% of GDP, from 2020 to 2024 on average 5%, in 2017-2019 about 4.4%, in 2010-2016 almost 3.7%, in 2003-2007 expenses amounted to 3.1%, and in 1995-2000 on average 2.9%.
U.S. GDP Share Lead States: California, Texas, New York
Growth according to official data on 2.8% in the third quarter
According to official data, US GDP grew by 2.8% in the third quarter of 2024. The data are probably falsified before the presidential election.
The economy's main driver of growth, consumer spending, was reported to have increased by 3.5%, the highest this year.
2.8% growth in Q2
US GDP in the second quarter of 2024 grew by 2.8%.
1.3% growth in Q1
The growth rate of the US economy in the first quarter of 2024 was lower than previously reported, which primarily reflects a decrease in consumer spending on goods.
The annual growth of US GDP in the first quarter was revised downward to 1.3% (1.6% earlier) and significantly weaker than the forecast (+ 2.5 %/earlier + 3.4%).
This figure is below the historical trend of 2010-2019 at 2.4% SAAR.
The US economy is out of consumer demand in the red by 0.09 pp in terms of contribution to GDP growth for the quarter with a long-term positive contribution of 0.83 pp.
Essentially, only consumer services are pulling the U.S. economy, everything else cumulatively in the red. Services are abnormal, since such or more significant growth was only once from 2010 - 4q14 (1.84 pp) without taking into account post-covid recovery from a low base.
State consumption and state investments provided only 0.21 pp and although this contribution is higher than the historical trend, from 3q22 to 4q23 the average positive contribution was 3.5 times more - 0.76 pp, providing more than a quarter of GDP growth. Now the state is coming off the stage or temporary clouding?
Imports are growing at a faster pace with weak export growth rates, which led to a sharply negative contribution of net exports at 0.86 pp (norm minus 0.15 pp) - this is the worst indicator in two years.
GDP growth forecast by 2.7%
On March 18, 2024, the American bank Goldman Sachs improved forecasts for economic growth and employment in the United States for 2024, taking into account the acceleration of immigration. Immigration beat the previous trend, Goldman said.
In 2024, the bank predicts US GDP growth of 2.7% in calendar terms.
2023
GDP per capita $77,000 per year
The second largest PPP GDP in the world
The US Economy Is Falling Back Again, Leaving Europe Fools
After the 2008 crisis, the largest macroeconomic trend was Europe's significant lag behind the United States. It was a big shift in the market. This led to deflation, the ECB QE and ultimately a significant fall in the euro/dollar from 1.40 to 1.05. Now it will be the same. The eurozone is lagging again, Bloomberg wrote in March 2024.
GDP growth of 135% over 20 years
GDP growth (at current prices) for the period 2003-2023:
China: 966%
India: 503%
Indonesia: 455%
Saudi Arabia: 395%
Russia: 303%
Brazil: 281%
Turkey: 265%
Canada: 136%
US: 135%
Germany: 77%
France: 65%
Italy: 38%
Japan: -6%
Real GDP growth for the year by 3.1%
US GDP grew by 3.3% in the IV quarter of 2023, ending an unexpectedly strong year. Later, in February 2024, the figure was reduced to 3.2%.
Real US GDP for 2023 grew by 3.1%, the highest since the first quarter of 2022.
The US estimate of GDP needs to take into account about 2 trillion budget deficits, so it would be inappropriate to talk about "phenomenal sustainability."
The budget deficit is most absorbed not on personal consumption, as it was in 2021-2022 through "helicopter money" and comprehensive incentives to households, but mainly on interest payments, bank assistance, defense and pensions.
4.9% growth in Q3
According to preliminary data from the Department of Commerce, the US economy in the third quarter of 2023 increased by 4.9%, this is the maximum growth rate since the fourth quarter of 2021.
Consumer spending rose 4%, the highest in nearly two years.
The world's largest economy remains resilient in the face of high prices and skyrocketing borrowing costs, repeatedly ahead of forecasters' expectations. The main driver of this resilience is the continued strength of the labor market, which continues to fuel demand from households.
On the other hand, US GDP growth is mainly driven by private consumption and inventories. This could prove short-lived.
The strength of consumer demand is due to a decrease in the saving rate to a historical minimum and accumulated savings during the period of fiscal and monetary rabies 2020-2021.
However, the real madness is that consumption is growing at a record in the face of extreme growth in the cost of consumer and mortgage loans at a declining rate of population income growth.
Change in statistics since 1947
In October 2023, a large-scale revision of American statistics was once again made... since 1947!
This could be expected on the basis of a large-scale revision of American income and spending data, and now the revision was on all key macroeconomic indicators in the entire US history! However, the main data transformation began in 2013 (before that, "cosmetic" changes).
If we touch the main indicator (GDP), we revised both nominal GDP and deflator. The discrepancy in nominal GDP was 0.85%, and in deflator - over 1% (underestimated total inflation). In addition to this, the statistics were given to the prices of 2017, and earlier the comparison was with 2012.
As a result, according to new data, the accumulated growth of the American economy over 10 years turned out to be almost 2% higher than according to old data. The most significant changes in crisis 2020 are now a drop of only 2.2%, while earlier it was believed that GDP fell by 3.4%.
2.1% growth in Q2
GDP USA grew by 2.1% in the second quarter of 2023 (forecast: 2.4%). What is the reason for the growth?
According to official data, the US economy not only overcame the consequences of urisis, COVID-19 but also practically reached the trending growth of 2010-2019, which was 0.54% on average for the quarter.
Since January 2022, the growth rate has fallen to 0.33% per quarter or 1.3% qoq in annual terms, but in the context of circumstances (the strongest inflation crisis in 40 years and the incredible pace of tightening of the Fed's monetary policy) growth looks impressive, Spydell Finance wrote.
However, from December 2019 to June 2023, with the decomposition of the components of US GDP growth, it turns out that the consumer sector made a dominant impact - out of 6.2% of US economic growth, the consumer sector contributed 6.25%, that is, all other components worked at zero (formally symbolic minus).
As for the consumer sector, since December 2019, the accumulated growth was 9%, where the consumption of goods increased by a record 17.3%, and the demand for services increased by 5.4%. Accordingly, goods contributed 4.1 percentage points to the total growth of US GDP by 6.2% from Q4 2019, and services contributed 2.1 percentage points.
Consumption of goods does not grow from Q2 2021 (as early as two years), and the main driver of consumer sector growth is services that compensate for the lag from the massive defeat in the era of COVID lockdowns.
The consumer sector in the United States from 2014 to 2019 had a share in GDP of about 68.7%, and from January 2022 on average 70.7%, i.e. an increase of 2 percentage points - this is a very significant change in such a short period of time.
Since the beginning of 2022, investments have been consistently declining and fell to the level of 2019 in real terms, and business is pursuing a fairly conservative investment and industrial policy, which affects the "burning" of reserves.
The trade balance is terrible (weak exports with significant imports), but better than in Q1 2022, although the stabilization has stopped since the beginning of 2023.
State investments are growing, but without fanaticism.
The reason for GDP growth since 2019 is the consumer sector.
Forecast growth of 1.3% for the year
Digital Economy, Finance and Services for Business Made Major Contribution to GDP Growth of 24% over 10 Years
What is driving the US economy? Over the past 10 years, US GDP has grown by 24%, but the growth figures themselves are little informative without understanding the factors driving the US economy, and this requires a decomposition of sectors in terms of contribution to GDP growth, Spydell Finance wrote.
A shorter period than 10 years does not make sense for comparison, since it is necessary to understand long-term trends, and a wider period will shift the focus from current trends. Next, not the weights of industries in the US economy will be demonstrated, but the contribution to growth over the past 10 years.
In the structure of the growth of the US economy by 24%, the private sector contributed 23.3 percentage points, and the public sector only 0.7 percentage points, that is, the private economy certainly dominates.
The manufacturing economy provided only 2 pp in 24% of the total GDP growth over 10 years, of which 0.65 pp is occupied by the production of computers, microelectronics and IT equipment. These calculations include: agriculture and forestry, fishing, mining, manufacturing, electricity and utilities. Accordingly, the service sector forms the main contribution to GDP growth.
The leading sectors in the service sector by contribution to US GDP growth in percentage points from Q1 2013 to Q1 2023:
- Professional and Business Services - 6.76
- IT, Telecommunications and Communications - 5.12
- Education and Medicine - 2.44
- Real estate, rent and leasing - 1.92
- Finance and Insurance - 1.48
- Retail - 1.11
- Wholesale - 0.97
- Transport and Warehouse - 0.51
- Hotels and catering - 0.50
- Culture, Sports and Entertainment - 0.34
- Other services - 0.11
- Construction - 0.03
If we take the IT sector, which includes both services and IT equipment production, the integral contribution to GDP growth over 10 years is 6 percentage points or ¼ from the total economic growth.
Finance, Insurance, Real Estate, IT, Education, Medicine, Professional and Business Services formed nearly 18 pp of the 24% US GDP growth over 10 years.
The producing economy has not been listed for a long time and a sharp tilt towards the digital economy, finance and servicing industries.
GDP growth relative to pre-COVID-19 level
Growth by 1.1% in Q1
U.S. economic growth slowed more than expected in the first quarter, as low business investment and declining inventories held back growth in consumer spending.
US GDP grew 1.1% in the first quarter of 2023 amid the highest consumer spending in nearly two years. Household spending grew at a rate of 3.7%.
The median forecast of a Bloomberg survey of economists suggested GDP growth of 1.9% and an increase in personal consumption of 4% on an annualized basis.
The consumer sector contributes the most to the formation of the US economy - the share of the consumer sector is almost 71% of GDP, compared with the average level of 68.7% between 2014 and 2019 and 67.8% from 2003 to 2008.
The resource in the growth of the share of the consumer sector from 2020 to 2021 was unsecured government spending within the framework of targeted subsidies to the population, redeemed by direct issue through the Fed printing press (helicopter money).
As the monetary and fiscal madness is turned off from 2022, the resource to support consumption at the achieved high level was savings, income growth ahead of inflation amid labor shortages and lending.
All consumption support factors have finished their main action or are neutralizing the positive effect, Spydell Finance wrote. For example, lending has been declining since March 2023 amid tightening credit conditions and rising rates, incomes have ceased to grow intensively in real terms, and savings are almost completely depleted for the population group in which savings determine consumption.
If we estimate long-term trends, current consumer spending on goods and services returned to the 2010-2019 trend, fully compensating for the covid failure.
The share of investments in GDP is decreasing, returning to the average level of 2014-2019. (details on the chart).
The share of net exports of goods and services after setting an anti-record in Q1 2022 (minus 7.5% of GDP) stabilized over the year, but by historical standards it is 1.5 pp worse than the norm.
The share of state participation in the economy through investment and state consumption was at the historically lowest level and increases slightly due to the military-industrial complex and infrastructure.
2022
GDP growth of 2.1% to $25.46 trillion or 25% of world GDP
The largest economy in the world in 2022 was still the United States with a nominal GDP of $25.46 trillion. The second place was taken by China ($17.94 trillion), the third - Japan ($4.17 trillion). Russia rose from 11th to 8th place with an indicator of $2.3 trillion, ahead of Canada and Italy.
inThe US accounts for 25% of global GDP.
The U.S. economy grew 2.1% for 2022, matching the 10-year average growth from 2010 to 2019 (2.2% for the year). In the year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the economy fell by 2.8%, but was flooded with an unprecedented amount of fiscal and monetary doping, in 2021 the growth was 5.9% on deferred demand and the implementation of the received liquidity from the Fed and the state.
In the structure of 2.1% of economic growth in 2022, almost all of the contribution was provided by consumer demand - 1.9 pp or over 90% of general economic growth. But the structure of consumer demand also matters, the Spydell Finance channel wrote.
Demand for goods made a negative contribution to 0.1 percentage points, and goods occupy approximately 1/3 of the turnover of the consumer sector. Services contributed 2 pp to the annual growth of the economy, i.e. we can say that the economy grew exclusively due to services, and all other components "worked" by zeros.
Services were the most affected by covid lockdowns, only in Q3 2021 services reached the base of 2019, while goods began to grow immediately, forced by helicopter money and the lack of purchase restrictions. Services in Q4 2022 are 4.2% higher than in Q3 2019, and demand for goods increased by 15.8%.
The shutdown of the helicopter money chopper, a significant increase in prices and a glut led to a halt in the growth of the commodity segment in 2022.
With investments, a difficult situation. Investment in residential real estate made a negative contribution to 0.5 pp - the worst dynamics since 2009! Investments in fixed assets made a positive contribution of 0.5 pp compared to 0.6-0.7 pp in the period from 2010 to 2019. There is no investment boom, business does not believe in the sustainability of demand and economic prospects.
Investments in general, taking into account reserves, made a positive contribution of 0.68 pp, and fully and completely increased due to the effect of reserves (+ 0.74 pp) Net exports contributed negatively to 0.4 pp, which is typical for the United States - they managed to sharply drown out imports from June 2022 and slightly increase exports.
Public consumption and investment contributed negatively to 0.1 pp for the first time since 2014 on the trajectory of spending cuts and budget optimization.
Second in the world in GDP by PPP after China
In August 2023, the World Bank updated its PPP GDP estimates for the world at the end of 2022.
Growth in Q4 by 2.9%
in GDP USA Q4, 2022 rose 2.9%, above analysts' expectations in 2.6%. Personal consumption, the largest part of the economy, grew 2.1% less than forecast.
Growth in Q3 by 2.9%
In the GDP USA third quarter of 2022, it grew by 2.9% compared to the previous period, which is higher than analysts' expectations in 2.7%.
GDP size forecast - $25.3 trillion
GDP contraction of 0.9% in Q2
GDP USA in the second quarter fell by 0.9%.
US, EU share of global economy shrinks
2021
GDP size - $22.94 trillion
US GDP up 5.7%
In 2021 GDP USA , it grew by 5.7%, this is the maximum increase since 1984. In 2020, US GDP fell by 3.4% (updated data released in January 2022), which was the largest drop in 74 years, according to data from the American Bureau of Economic Analysis. Departments of Commerce
High economic growth in the United States was also accompanied by high inflation. In 2021, it accelerated to 7%, which was the largest indicator since 1982. Against this background, the US Federal Reserve announced the termination of anti-crisis measures. A tighter monetary policy is expected to contain price increases well above the 2% target.
At the end of January 2022, the US Federal Reserve kept the key rate at 0-0.25%. The management expects that with inflation rates noticeably above 2% and a strong market, it will be appropriate to raise the rate.
Increased consumer spending was holding back shortages of vehicles and other goods amid manufacturing woes due to a global shortage of semiconductors, Reuters reported. Among the factors that also contributed to curbing consumer spending growth in 2021: dwindling household purchasing power and inflation.
The increase in private investment in inventories was due to retail and wholesale trade. In the retail sector, the main contribution was made by the investment of car dealers in inventories. The growth in exports reflected an increase in both goods and services. The increase in exports of goods was widespread in 2021, and the main contribution to it was made by consumer goods, industrial goods and materials, as well as food, feed and drinks. The increase in service exports came from travel.
In general, in 2021, the volume of exports increased by 24.5%, imports - by 17.7%.[1]
Average annual GDP growth over 40 years - 2.6%
GDP per capita $69.2 thousand
In 2021, Chinese GDP per capita remains significantly lower than American GDP.
2020
Record decline in GDP since World War II - in 3.5% amid COVID-19 pandemic
At the end of January 2021, it became known that in 2020 in the United States there was a record decline in GDP since the Second World War. If in 1946 the economic decline amounted to 11.6%, then in 2020 - by 3.5%. In addition, this is the first decline in US GDP in a year since 2009 - then the figure dropped by 2.5%.
The reason was the COVID-19 pandemic, which reduced consumer spending and business investment, leaving millions of Americans out of work.
The decline in 2020 was noted in almost all sectors, with the exception of the public and housing markets. Consumer spending, which accounts for more than two-thirds of the economy, fell 3.9%, its worst since 1932. Only 12.4 million of the 22.2 million jobs lost in March and April were restored by early 2021.[2]
Over 20 years, US GDP has grown by 108%.
2nd quarter: the strongest decline in GDP in history amid the COVID-19 pandemic: -32.9%
According to data published by the Bureau of Economic Analysis under the Ministry of Commerce, in the second quarter of 2020 GDP USA it collapsed immediately by 32.9% compared to the previous quarter (in annual terms). This is the sharpest collapse of the American economy in the entire history of observations of the dynamics of GDP - that is, since 1947. The current decline has crossed out all growth in the US market since 2015.
The previous anti-record was recorded in 1958, when the US economy contracted by 10.0%. In the 4th quarter of 2008, at the peak of the global financial crisis, US GDP fell by 8.4%.
The reason for the collapse of GDP was the pandemic crisis of the coronavirus COVID-19, or rather the sharp drop in personal consumption due to it, a deterioration in the business climate and a decrease in business income.
The main locomotive for the development of the American market is personal consumption - it generates about 70% of US GDP. In the second quarter, its volumes decreased by 10.1%. Most of all, Americans cut spending on services (especially, surprisingly, in the healthcare sector) and mass-demand goods (especially on clothes and shoes).
4.8% decline in the first quarter
According to the US Department of Commerce, in the first quarter of 2020, US GDP decreased by 4.8% compared to the same period in 2019.
There has not been such a strong decline since the beginning of 2014. And this is the most serious drop since the end of 2008: then in the last quarter, US GDP fell by 8.4% on an annualized basis.
That beat forecasts from economists polled by Reuters. They expected a reduction in US GDP in January-March 2020 by about 4% year-on-year. Although some of them even believed that the decline could be 15% and become a record in history. At the same time, the measures taken to combat the spread of coronavirus and practically paralyzed the country's economy were in effect only in the last weeks of the quarter, and before that business activity was normal.
Until this year, the US economy experienced the longest period of growth in its history with an average pace of about 2%, it lasted 11 years. In the first quarter of 2019, the country's GDP growth in annual terms amounted to 3.1%, in the second - 2%, in the third - 2.1%, in the fourth - also 2.1%.
In the first quarter of 2020, consumer spending in the United States decreased by 7.6%, imports decreased by 15.3%, and exports - by 8.7%. The coronavirus pandemic and social isolation measures had a negative impact on the American economy.
| This led to rapid changes in demand, as enterprises and schools switched to remote operation or canceled their operations, and consumers canceled, limited or redirected their expenses, the Ministry of Trade said in a statement. |
The rise in the PCE Core index (Personal Consumption Expansions, Excluding Food & Energy), which closely monitors the Federal Reserve when assessing inflation risks, accelerated to 1.8% in January-March from 1.3% in the previous three months.[3]
2018
World leader in terms of nominal GDP
GDP per capita more than $55 thousand
The GDP of PPP of US cities is comparable to the GDP of individual countries
2017: Pay's share of GDP shrinks
Main article: Salaries in the United States
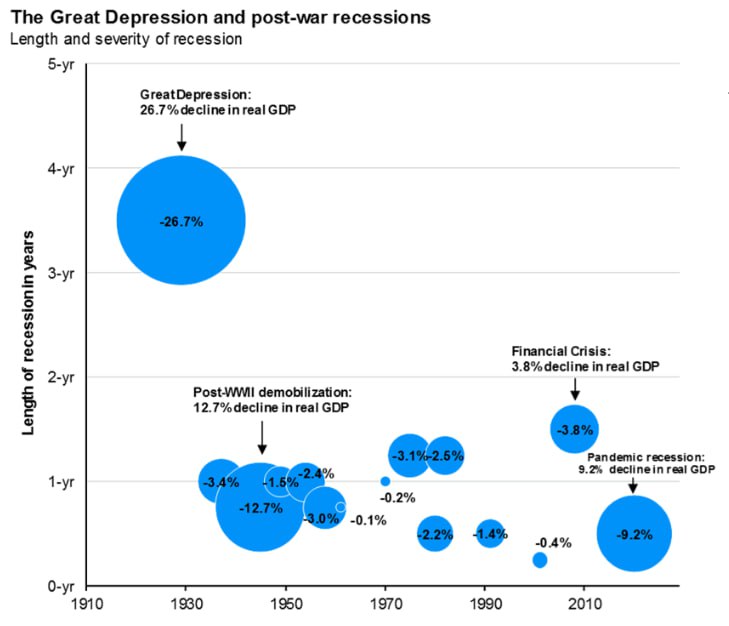
1930s: A 26% drop in GDP is the largest crisis in US history
No crisis in US history is comparable in scale to the Great Depression of the 1930s. Real US GDP collapsed by 26.7% in just a few years, and the unemployment rate exceeded 25%.
According to Milton Friedman, the key mistake was that the Fed did not provide the banking system with liquidity, allowing massive bank bankruptcies and compression of the money supply by ~ 30%. That's what turned a recession into a protracted depression.
Binding to the gold standard limited the possibility of easing policy - central banks could not expand the money supply, fearing the outflow of gold.
An additional blow was the Smoot Hawley Tariff (1930) - the United States increased import duties, causing a trade war and a collapse in global exports by more than 60%.
The parallel with that in the meantime is that in 2025 many political decisions are made in the United States, which over time may turn out to be catastrophic mistakes - as was already the case in the 1930s.
1918: World War I GDP growth of 108%
The main winner in World War I was the United States, which more than doubled its GDP in five years of war! Britain's GDP also grew by 15%, but continental Europe was in ruin.
The hardest hit France (-36% of GDP) and (Russia -32%)., although Germany losing in the war, lost only 18% of GDP.